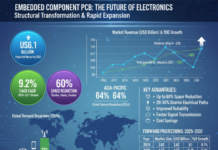
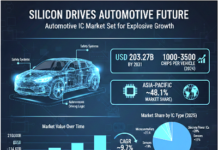
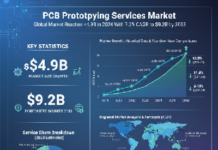
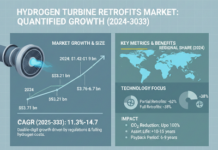
Market Summary:
According to our latest research, the global wearable electronics materials market size reached USD 3.21 billion in 2024. The market is expected to grow at a robust CAGR of 14.8% from 2025 to 2033, projecting the market to reach USD 10.19 billion by 2033. This remarkable growth trajectory is primarily driven by surging demand for smart wearable devices across healthcare, fitness, and consumer electronics sectors, as well as rapid advancements in material science that enable the miniaturization and enhanced performance of wearable technologies.
Market Overview
The market for wearable electronics materials encompasses a range of substances such as polymers, conductive fabrics, silicones, graphene, and flexible substrates. These materials are specifically engineered to be lightweight, durable, flexible, and biocompatible, ensuring both functionality and user comfort. Rapid advancements in miniaturization technology and the integration of sensors have accelerated the adoption of high-performance materials in this sector.
Key Drivers of Market Growth
1. Increasing Adoption of Smart Wearables
The surge in health-conscious consumers and the rising trend of personal wellness monitoring have boosted demand for devices like smart fitness bands, heart rate monitors, and ECG-enabled wearables. This directly fuels the need for high-quality materials that enhance device longevity and performance.
2. Advancements in Flexible and Stretchable Electronics
Technological breakthroughs in flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), stretchable conductive inks, and wearable fabrics have broadened design possibilities. These innovations enable the creation of wearables that conform to the human body without compromising performance.
3. Integration of AI and IoT in Wearables
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities has increased the complexity of wearable devices, necessitating materials with better conductivity, improved thermal management, and higher durability.
Material Segmentation in Wearable Electronics
1. Conductive Polymers
These are widely used due to their ability to provide lightweight conductivity while maintaining flexibility. They are critical for integrating sensors into textiles and skin-contact devices.
2. Flexible Substrates
Materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyimide (PI) serve as substrates for flexible circuits, enabling thinner and lighter designs for wearable devices.
3. Graphene and Nanomaterials
Graphene’s exceptional electrical conductivity and mechanical strength make it a game-changing material in high-performance wearables, especially in energy storage and flexible displays.
4. Biocompatible Silicones
Used in medical wearables, biocompatible silicones offer skin safety, water resistance, and long-term comfort.
Applications of Wearable Electronics Materials
1. Consumer Electronics
From smart glasses to VR headsets, wearable materials play a key role in ensuring comfort, reducing weight, and enhancing device durability.
2. Healthcare and Medical Devices
Materials in medical wearables must meet stringent safety standards while allowing accurate biometric monitoring, such as in insulin delivery systems and ECG monitors.
3. Sports and Fitness
Smart clothing embedded with motion sensors uses stretchable and breathable fabrics that improve comfort during workouts while collecting performance data.
4. Industrial and Military Wearables
Rugged and heat-resistant materials are essential for wearables designed for harsh environments, such as smart helmets and augmented reality visors.
Challenges Facing the Market
1. Material Durability and Longevity
Frequent bending, stretching, and exposure to sweat or moisture can degrade materials over time.
2. Cost Constraints
Advanced nanomaterials and biocompatible compounds can be expensive, limiting mass adoption in low-cost consumer wearables.
3. Sustainability Concerns
The need for environmentally friendly, recyclable materials is growing as e-waste becomes a global issue.
Future Outlook
The future of wearable electronics materials lies in smart, adaptive materials capable of self-healing, energy harvesting, and advanced biometric sensing. With ongoing research into nanotechnology and printed electronics, the next generation of wearable devices is expected to be thinner, more flexible, and seamlessly integrated into daily life.
Source: https://researchintelo.com/report/wearable-electronics-materials-market