Medical electronics continue to change the face of healthcare radically by making the ongoing, based monitoring possible, early disease detection feasible, and treatment more personalized. The two main revolutionary changes in medical electronics are wearable diagnostics and implantable IoT devices. These technologies integrate sensors, connectivity, and data analytics to deliver real, time health insights, thereby revolutionizing the management of care between patients and healthcare providers.
The Rise of Medical Electronics in Modern Healthcare
Medical electronics are electronic devices and systems meant for diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment. Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) has made these systems more intelligent and connected. Both hospitals and home healthcare are using connected medical devices more and more to keep an eye on patients’ health metrics outside the regular clinical settings.
Wearable and implantable devices will play an important role in this transition. They facilitate the gathering of data on a continuous basis, thus they are a support to preventative healthcare and help clinicians make decisions based on evidence. This development is a manifestation of a wider trend toward patient, centered care and remote health monitoring.
Wearable Diagnostics: Expanding Real-Time Health Monitoring
How Wearable Medical Devices Work
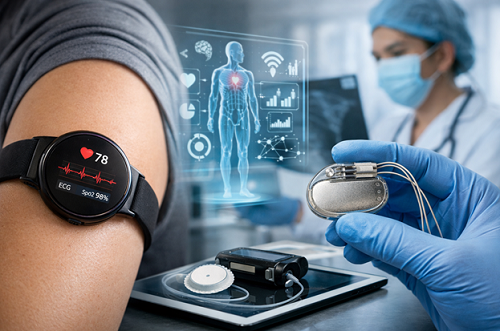
Wearable diagnostics cover smartwatches, biosensors, and medical grade wearable monitors that measure physiological signals, e.g., heart rate, oxygen saturation, and physical activity. These wearable medical devices incorporate sensors and wireless communication to send data to smartphones or cloud platforms.
Nowadays, some very sophisticated wearables are fitted with artificial intelligence that helps them to analyze patterns and spot anomalies in the data. Take for instance, a few gadgets that are capable of detecting irregular heart rhythms or sleep disturbances and alerting the users to consult a doctor. This incessant flow of data paves the way for timely intervention as well as ongoing health care.
Benefits of Wearable Diagnostics in Healthcare
Wearable diagnostics offer several practical advantages:
- Continuous monitoring: Patients can track vital signs in real time.
- Early detection: Subtle physiological changes may indicate emerging health issues.
- Improved patient engagement: Individuals gain greater awareness of their health.
- Remote patient monitoring: Healthcare providers can review data without requiring frequent in-person visits.
These features are particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. By enabling proactive care, wearable health technology reduces hospital readmissions and improves quality of life.
Implantable IoT Devices: Advancing Precision Medicine
Understanding Implantable Medical Electronics
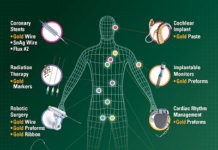
Implantable IoT devices refer to electronic systems inserted into the human body to keep track of or control the physiological functions. Examples of such devices are pacemakers, neurostimulators, and implantable glucose monitors. These implantable medical devices in healthcare have a wireless communication feature with an outside system, thus enabling clinicians to remotely get the performance data and make necessary adjustments.
Current implantables are developed to consume less power and be compatible with the human body. Innovations in reducing the size of components and energy storage have resulted in devices becoming not only smaller but also safer and more reliable.
Clinical Applications and Impact
Implantable IoT devices are key to the effective treatment of complex medical conditions. In cardiology, smart pacemakers are capable of not only adapting to the patient’s level of physical activity but also of sending diagnostic data to doctors. Implants used in the brain for neurological conditions, after delivering targeted electrical stimulation, are able to assist with the management of chronic pain or movement disorders.
These devices help to change healthcare into precision medicine. By personalizing therapy based on constantly collected data, personalized therapy can be at its best and long, term outcomes can be facilitated.
Data Security and Ethical Considerations
The leading source of concern with medical device cybersecurity and patient privacy has been the widespread use of connected healthcare devices. As wearable and implantable systems collect very sensitive personal information, strong security measures have to be implemented.
On the one hand, manufacturers, and on the other, healthcare organizations, are expected to implement enough safeguards such as encrypting data, using secure authentication, and updating software regularly to protect patients’ data. In addition, there are ethics regarding data ownership and whether permission has been properly granted. Without a doubt, the public will continue to trust in the digital health world only if there is a clear set of policies, adequate regulatory oversight, and transparency.
Challenges and Future Directions
Besides their potential, wearable diagnostics and implantable IoT devices still have to deal with a number of issues. The performance of a device can be influenced by technical limitations such as battery life, sensor accuracy, and interoperability. The regulatory approval process is intricate due to the necessity of safety and effectiveness be ensured.
Future development of wearable biosensors will be largely defined by technological progress. Systems with flexible electronics, advanced biosensors, and AI, driven analytics may be capable of substantially increasing the functionality of devices. The collaboration with telemedicine platforms, no doubt, will enhance the availability of healthcare, in particular, for the isolated and the marginalized areas.
In addition, scientists are investigating the prospects of state, of, the, art wearable and implantable medical devices that are fused with the human body without a trace. Such breakthrough technologies will allow extremely accurate monitoring and the use of adaptive therapies, thereby the whole healthcare approach is leveled up from reactive to predictive and preventive.
Conclusion
Wearable health devices (with some exceptions) and implantable Internet-of-Thigs (IoT) devices are revolutionising the modern healthcare systems and creating a method for provider-centred medical professionals to track patients continuously, deliver highly personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s data and provide care through means of remote monitoring.
While obstacles exist (e.g. security of data transfer, regulation issues, interoperability, etc.) as they grow and develop through continual efforts involving innovation and implementation in telehealth practices.
As healthcare continues to expand through the implementation of connected medical devices, technologies will see an increased use of information-based clinical decision making through the use of data in the rhythm of day-to-day clinical practice. The future of medicine and how we use it to assist in providing excellent patient care will depend on the progression of medical electronics.