A well-organized industrial network operates efficiently within every control panel. At the system’s core is an AC-to-DC power supply, which converts incoming AC line voltage—whether 120V, 240V, or 480V—into a stable 24VDC of output current.
Over time, 24VDC became the de facto standard for low-voltage output power in most modern industrial control systems, simplifying component integration, maintenance, and replacement. As a direct current source, 24VDC is less prone to electrical noise and voltage drops, making it ideal for powering precision control and monitoring equipment. Additionally, it qualifies as a Safe Extra Low Voltage (SELV), helping to minimize shock risks and eliminate arc flash concerns.
The Need for Higher Output Voltage
While most industrial automation devices, including sensors, actuators, I/O modules, HMIs, and PLCs, operate on 24VDC, some components require higher DC input voltages. For instance, industrial PoE switches compliant with IEEE 802.3bt/af/at standards typically operate at 48VDC-57VDC, along with most routers, base stations, and servers.
Beyond industrial automation, higher voltage requirements extend to applications such as IP cameras, LED lighting, and environmental sensors—especially in solar-powered systems relying on 12V-36V from battery storage. A prime example is mobile security trailers equipped with solar panels. Similarly, smart buses, trains, and electric vehicles require higher power levels to support onboard climate control, driver assistance systems, and infotainment without overburdening power supplied from 12V-36V battery banks.
The Role of DC-to-DC Power Boosters
External DC-to-DC converters offer a practical and efficient solution to meet higher power demands. Step-up converters are compact, reliable, and energy-efficient, enabling the integration of higher frequency and voltage devices without requiring an entirely new power infrastructure.
Evolution of Voltage Boosting Technology
The need for power and voltage conversion dates back to the early 20th century, when Edison’s DC power distribution was converted to AC using large rotary converters. The development of DC-to-DC conversion emerged in the 1960s for aerospace applications. Initially, boosting DC voltage involved converting it to AC, applying it to a step-up transformer, and then rectifying it back to DC—a process that was both inefficient and costly.
Modern switched-mode DC-to-DC boost converters have transformed this process. By temporarily storing input energy during the switch-on phase and releasing it at a higher voltage than input, during the switch-off phase, these converters achieve up to 99% efficiency. The basic design of boost converter consists only of an inductor, semiconductor switch, diode, and capacitor— an improved solution that maximizes energy efficiency.
Many industrial network devices now integrate internal DC-to-DC boost converters including managed and unmanaged PoE switches. However, not all devices include built-in voltage boosters, making external solutions necessary.
Choosing the Right DC-to-DC Boost Converter
Selecting the ideal DC-to-DC boost converter requires careful consideration of several key factors:
- Power Requirements: Identify the rated power the device needs, as specified in its documentation or power supply label.
- Input Voltage: Verify the available input voltage, such as a 12VDC battery or 24VDC control panel supply. A versatile converter should support a broad input range (e.g., 9-36VDC) with an adjustable output voltage to accommodate multiple components in various applications.
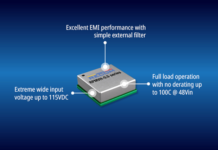
- Power Protection: Ensure the converter includes safeguards against short circuits, overload, reverse polarity, and undervoltage to maintain system stability and prevent damage.
- Industrial Design: Look for a robust, certified design that withstands harsh environments and high temperatures. A compact form factor is essential for easy installation on densely populated DIN rails.
DC-to-DC Boost Converter Solutions
As industries embrace automation and IoT-driven technologies, demand for higher frequency and voltage power solutions continue to grow. Strictly regulated DC power is vital for optimizing Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), yet many engineers struggle to find suitable high-voltage solutions within their control cabinets. For expert guidance on selecting the right power solution for your application, contact Antaira’s technical team at (714) 671-9000 or email sales@antaira.com.
For more information, visit antaira.com.