Instrumentation and Monitoring of the metro helps to mitigate great risks of life and property. Since the metro runs from various areas, it is crucial to judge, monitor, and provide remedies for the effective construction of long metro tracks.
One of the largest challenges is the construction of underground tunnels that run through many residential areas. It is important to minutely monitor using various geotechnical instruments to accurately judge the possibility of every mishappening.
Dubai metro is one such project which was handled by Encardio-rite during their two phases. Let’s discuss the project overview and Encardio’s scope of work for the same.
Dubai Metro Project Overview
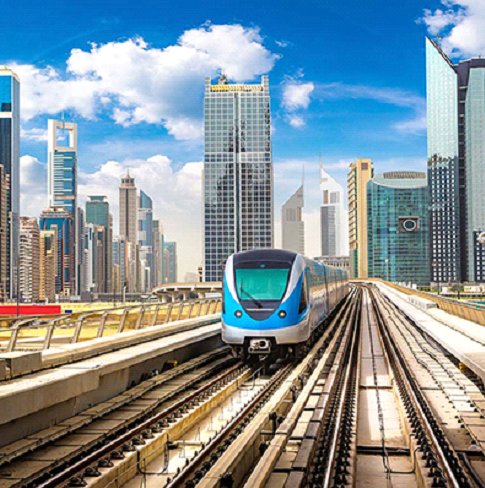

Dubai Metro Project is the first urban metro to operate in the Gulf’s Arab States and is the longest automated driverless system in the world. The metro currently runs on two lines (Red and Green), moving underground through the city center or on elevated viaducts. The metro has 45 stations, 2 depots, and several operational centers.
The Red line runs through Al-Rashidiya to Jebel Ali which is a 53km long track with 26 stations. Out of these, 4 underground stations (tunnels) run through the course of 5.6 km. The Green Line is active from Al-Qusais to Al-Jadaf, running through 18 km with 14 stations, out of which 7.9km consists of underground (tunnels).
The overall route runs underground in the city center from the Sheikh Rashid/Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed intersection to Salahuddin/Abu Bakr Al Siddique intersection on Red line and from Garhoud to Oud Metha Road on Green line.
Encardio-rite Monitoring Solutions for the Dubai Metro Project

Encardio-rite handled the complete monitoring and surveying solution for the entire project. It was awarded the I&M sub-contract by DURL consortium consisting of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Mitsubishi Corporation, Obayashi Corporation, Kajima Corporation, and YapiMerkezi.
The monitoring solutions were provided for the following:
- Underground stations,
- Tunneling sections, and
- Structures falling within the zone of influence (Red and Green Line)
Encardio-rite Turnkey Services for Dubai Metro Project

Encardio-rite provided the following turnkey services for 4 years until the completion of the project:
- Supplying the geotechnical instruments needed during the completion of the project.
- Conducting Optical Survey and Monitoring
- Providing with daily, weekly and monthly reports with evaluation and interpretation.
- Installing the geotechnical instruments which included the drilling works for subsurface instruments.
- Calibration of data loggers and sensors
Geotechnical Instruments used in the Dubai Metro Project

- Inclinometer: Used to monitor lateral movements behind the diaphragm wall, in diaphragm walls and in monitoring arrays that resulted from excavation and tunneling works.
- Standpipe piezometer: Used to monitor groundwater level encompassing the station area and across tunnel alignments.
- Magnetic extensometer: Used to monitor subsurface settlement that occurs at various depths due to excavation and tunneling.
- Strain gauges and load cells: These are fixed in struts to calculate the stress while preloading and during excavation.
- Surface settlement points: Used to monitor surface settlement by installing them in soil and pavement across tunnel alignment and nearby excavation work.
- Building settlement points: Installed on structures/buildings within Zone of Influence to monitor settlement
- Tilt meters: Situated on walls, floor slabs, supporting frames to monitor uniaxial or biaxial rotation or angle of tilt of buildings and structures within Zone of influence.
- Crack gages: Used to determine any change in the width of existing cracks of building and structures close to the construction activities.
Monitoring reports were provided by Encardio which included the observation of variations in data and listed out the factors for the same.
The reports also included progress charts that gave tunnel excavation details with respect to the monitoring data.