FASTag – A smarter way of Toll Collection:
The idea of Electronic toll collection (ETC) came from Japan and China who adopted it in the year 2001 and 2014 respectively. In India, the concept was decided to implement in the month of April 2013 and the Scheme of ‘One Nation One FASTag’ came into force on 15 December 2019.
To prevent the overcrowding of traffic, air pollution and to ensure a smooth transportation on National highway’s Toll plazas, the NPCL (National Payments Corporation of India) has introduced FASTag as a nationwide Electronic Toll Collection solution which has become compulsory on Fastag-only lanes and presently it is operational at 240 plus toll plazas across national & state highways.
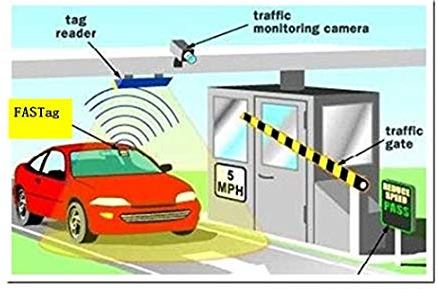
FAS Tag is a vehicle-specific and RFID Technology-based device which enable digital cash transaction for paying toll-fare while being a vehicle in motion. It is an RFID tag fixed on the windscreen of a vehicle which enables electronic toll collection immediately from the registered bank account of the car owners without stopping them for payment.
The Road Transport and Highways Minister, Mr Nitin Gadkari announced that from January 15, Fastags will become mandatory for payments at all toll plazas for all vehicles, private and commercial. In order to make the payment method more easier and appropriate the Reserve Bank Of India recently confirmed that any of the authorized payments methods like Google Pay, PhonePe App or BHIM can be linked with Fastag and can be used to recharge it.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) A Technology behind FASTag:
RFID is a technology behind Fastag which uses radio frequency waves to track the items and transfer the data without being in contact by reading and capturing the information stored on a tag which is attached to the object.
RFID tags consist of – tags or labels which are rooted with a transmitter and a receiver, an antenna which transmits and receive a signal, a microchip to processes and stores the information and an interrogator (two-way radio transmitter and receiver) which transmit the results to an RFID computer program.
When the vehicle reaches the toll plaza, the RFID antenna at the top of the toll gate scans the tag identification number and the QR code and then lift the barriers to allow a vehicle to pass through.
Types of RFID tags:
- Passive RFID tags (used in FASTag): Passive RFID tags are those tags which operate without a battery and get power supply from the electromagnetic energy transmitted by the RFID reader.
These tags are long lasting and have more economical value due to lower cost of manufacturing. It is employed in many industries for file tracking, supply chain management, race timing and smart labels etc.
- Active RFID tags (battery-powered): Active RFID tags operate through a small battery that powers the relay of information. These have a short time span and need to be replaced when the battery dies.
It has the longest communication range, more expensive than the Passive RFID tags and is capable of performing diagnostics and initiating the communications.
FASTag Benefits:
- It is a reloadable tag which is simple to use.
- Reduces the overcrowding and waiting time at toll plazas.
- Prevents air pollution which occurs due to congestion around toll plaza.
- Facilitate ease of transaction through digital payment of toll-fare.
- Saves the travel time and fuel consumption.
- Provide secure interoperable framework applicable across the country.
- Eco-friendly initiative as it reduces pollution and use of paper.
- Better highway management and reduced efforts in managing toll plaza.
- A web portal for all the customers to access their statements of transaction by logging on the FASTag customer portal.
- SMS alerts for the transactions on the registered mobile number of the customer.
- Online recharge facility by using any of the authorized method of payments and bank linked to the FAStag.