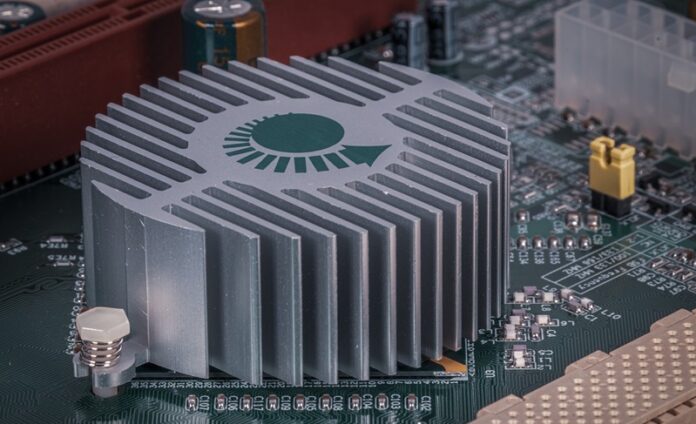
Heat sinks play a crucial role in managing and dissipating the heat generated by electronic components. As a result, they are an essential element of all electrical devices that guarantee optimal performance and prevent overheating.
Nevertheless, once you need to choose heat sinks for your application, you have to decide which type of heat sink will be the most accurate – passive or active. Let’s then check what those are and what their use cases are to make your decision easier.
What are Passive heat sinks?
Passive heat sinks are based on the principles of natural airflow to dissipate heat. Therefore, they don’t entail fans, blowers, and other active cooling mechanisms in their infrastructure. As a result, they are perfect for silent, noise-sensitive environments.
Moreover, one of their main advantages is the fact that they are energy efficient as they don’t consume any additional power. They also have a longer lifespan and better reliability when compared to their active counterparts, as they don’t entail any moving parts.
Nevertheless, it is worth mentioning that they may be less efficient at cooling high heat loads and may not be suitable for applications with extreme thermal demands.
What are the best use cases for passive heat sinks?
In fact, there are numerous applications for passive heat dissipators, among others:
- industrial computers where debris and dust could damage fans,
- low-power electronics, for example, IoT sensors and embedded systems, which can benefit from passive cooling to save energy,
- home theater PCs that can easily maintain a quiet and unobtrusive entertainment experience with this type of sink.
What are active heat sinks?
Unlike passive heat sinks, active ones utilize fans or blowers to enhance heat dissipation. Such fans force air across the heat sink’s fins, increasing the rate at which heat is transferred from the electronic component to the surrounding environment.
As a result, active heat sinks provide efficient cooling, especially in situations where high heat loads are generated. They are suitable for:
- electronic devices with limited space, as they don’t require a large heat sink,
- temperature-sensitive applications, as they are great at controlling temperature.
Nonetheless, they consume more power and generate more noise than passive heat sinks.
What are the best use cases for active heat sinks?
Active heat sinks are commonly used in gaming laptops to manage the heat generated by powerful GPUs and CPUs.
They are also employed by data centers and server rooms to cool multiple high-performance servers. Last but not least, they can be used by workstations with demanding tasks such as 3D rendering and video editing.
Summing up, passive heat sinks are perfect for scenarios where silent operation, energy efficiency, and reliability are crucial. On the other hand, active heat sinks are more suitable for high-performance devices that require efficient cooling and precise temperature control. It is advisable then to reflect on your requirements and choose the ones that will be more suitable for your specific application.