Fujitsu announced the development of a new technology to make collaboration between robots and humans easier, safer and more efficient. The spatial world model technology makes it possible for AI to predict the future behaviors and states of different actors and objects within a space, and facilitates smooth collaboration between humans and robots, as well as optimal coordination among robots. This new development comes as part of Fujitsu’s broader research and development efforts in the field of physical AI.
The spatial world model technology will be showcased at CES2026, held in Las Vegas from January 6 to January 9, 2026. Fujitsu also plans to conduct technical demonstrations at its headquarters during fiscal year 2026.
Spatial World Model Technology Features
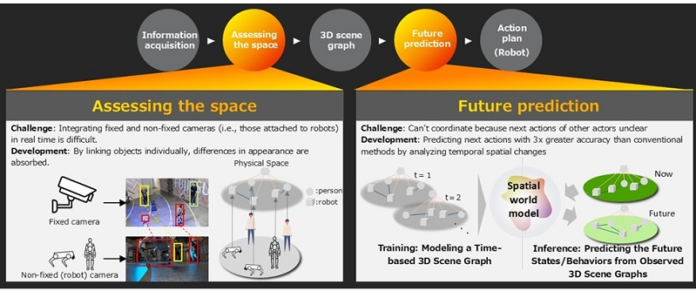
- Construction of a spatial world model using 3D scene graphs focusing on human, robot, and object interactionsIn physical environments, the spatial situation changes dynamically as actors within the space (i.e., people, robots, etc.) move and act. While technologies that use capturing data from cameras to understand these spatial dynamics have been explored, significant differences in the range captured by each camera and variations in appearance (such as distortion) between fixed and mobile cameras has made it difficult to achieve this in real time. Therefore, instead of pixel-level integration, which is highly susceptible to differences in appearance, Fujitsu developed a technology that uses cameras to assess the space using 3D scene graphs, i.e., hierarchical data structures that organize all objects in the physical space as points on a graph. This approach minimizes the impact of field of view and distortion, enabling real-time understanding of complex, dynamically changing real-world spaces.
- Prediction of future states/behaviors by modeling the interactions of people, robots, and objectsFor humans and robots to be able to work together smoothly, robots have to be able to understand the intentions behind human actions and predict how they will behave in the future. World model technologies that enable robots to predict changes and act in their immediate surroundings are being widely researched, but so far they have been limited to modeling only the immediate environment and have not yet been able to grasp the dynamic changes throughout an entire space.
Fujitsu’s newly developed method accurately estimates behavioral intentions by interpreting causal relationships from the diverse interactions between actors and objects in a space. By using this data to predict future actions, the technology can help to avoid collisions and generate optimal cooperative action plans for multiple autonomous robots.
In academic public benchmark data tests, it was confirmed that this technology can improve the accuracy of estimating behavioral intentions by 3x.
Background
AI technology, which has primarily developed in digital spaces, is now being applied to real world scenarios. “Physical AI” is a field of AI technology where AI is trained to understand physical laws and act autonomously and it will play a key role in solving various real-world challenges, such as in autonomous driving and smart factories. It is attracting significant attention as a potential means of helping with Japan’s worsening labor shortage and improving industrial productivity.
However, current physical AI applications are mainly limited to structured environments with defined pathways like manufacturing sites or logistics warehouses. In residential homes and offices, where human movements are less predictable and object arrangements frequently change, it is difficult to for AI to assess spatial dynamics, making current solutions impractical. Furthermore, in environments where large numbers of people and robots must work together, cooperation is currently difficult because the AI cannot understand the intentions behind others’ movements.
This new technology is based on Fujitsu’s Computer Vision technology, primarily used for human flow analysis in commercial facilities and abnormal behavior detection in crime prevention, as well as its digital AI technology, including the Fujitsu Kozuchi AI Agent which autonomously carries out tasks with human counterparts. It is part of the research efforts of the Spatial Robotics Research Center which Fujitsu established in April 2025 to step up its research toward realizing a new society where humans and robots coexist.
For more information, visit global.fujitsu.