In our increasingly digital world, we often hear various buzzwords describing game-changing technologies that are set to change the way we live, work and play. Undoubtedly, the Internet of Things has already started redefining how we go about our everyday lives.
What exactly is the Internet of Things, or IoT? It’s about connecting things through embedded sensors – in everyday items like toothbrushes and clothing to machines and buildings.
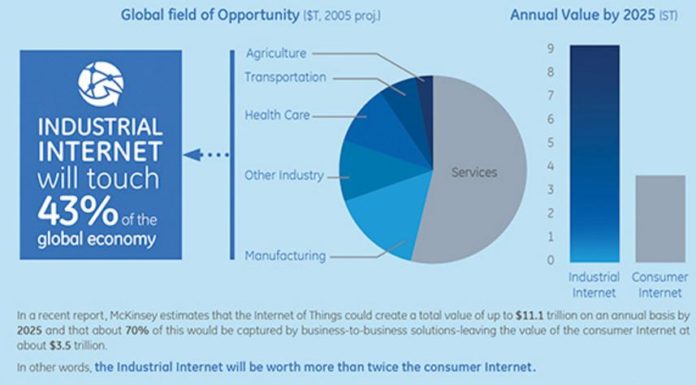
On an industrial scale, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can provide insights into customer behaviour, machine performance, and streamline tasks – ultimately raising efficiency, convenience and productivity while dramatically enhancing the quality of living and transforming the way we experience products and services around us.
IIoT has the potential to transform emerging economies like India, especially as we start to see the average cost of sensors continue to drop, further driving the proliferation and development of connected devices. In fact, the Indian government envisions creating a market of $15 billion by 2020, increasing connected devices by more than 13-fold to 2.7 billion units by then, according to NASSCOM.
With the industrial world primed for digital transformation, IIoT is already disrupting and redefining how companies operate their businesses. While the impact is varied depending on the sector, there are a few common patterns in their adoption. Firstly, in today’s fast paced business environment, companies are adapting to become more agile and understanding how to leverage real-time data to deliver more relevant solutions. Secondly, they see the potential to optimize processes through the data collected which can help to pre-empt demand.
Here are four key industries which IIoT continue to revolutionise:
1. Power
What if you could use advanced analytics to predict events before they happened? Power companies such as Scottish and Southern Energy (SSE) are doing exactly that through digital analytics. Leveraging a network of sensors which are monitoring over 1,000 assets across its facilities, SSE has been able to turn data into actionable insights to empower its engineers. This includes for example predictive analytics that allow workers to pre-empt problems to avoid unplanned outages – helping it currently to save nearly $4 million annually as well as reducing insurance costs by over $6 million per year.
Besides extending the life of equipment, connected power plants also have the potential to be greener as they can help integrate renewables in the long term. This is made possible because smarter plants are more flexible and better able to respond to fluctuations in the power supplied by intermittent sources like wind, water and solar. Improved connectivity means higher agility, allowing power plants to better control the mix of their output more efficiently – ramping up fossil fuel generation as required when natural sources are inadequate.
Using tools such as GE’s software platform Predix and Asset Performance Management (APM), power plants can move from reactive to proactive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime, minimize maintenance costs, improve efficiency, and extend asset life.
2. Transportation
Whether it’s moving goods or people, transportation is the backbone to the smooth operation of any economy or society – directly and indirectly affecting areas such as productivity, commerce, social, and health.
Railroads are one area with a huge potential to transform. Many railroads are already struggling with congestion, breakdowns, and sluggish speeds on many routes. Amid rising urbanization, there is likely to be growing challenge in meeting increased demand that will put a strain on existing infrastructure.
How can we solve this? One answer lies in creating transportation systems that can sense and respond dynamically to real-time conditions.
This can be achieved in the industry through software such as GE’s RailConnect 360, a portfolio of connected solutions that offers customers data-driven insights to help optimize assets, networks, and operations. U.S.-based Norfolk Southern Railway is currently using this solution, which has helped it improve its network velocity by 10 percent and improved its staff efficiency.
By analysing real-time data from engines and sensors monitoring the environment – such as temperature, humidity, weather forecast, traffic – transport networks can become more efficient as well as safer.
3. Aviation
IIoT is also poised to transform the travel experience up in the air. There are multiple opportunities to improve operational efficiency and offer increased personalisation to airline passengers.
Among airlines that have started experimenting with IIoT, there are projects to improve passenger experience, baggage handling, equipment monitoring, and generating fuel efficiencies.
AirAsia is one example of an airline leveraging data and analytics to drive customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. With a growing fleet of more than 160 aircraft, it operates at least 340,000 flights per year to more than 100 destinations in over 20 countries.
The airline is leveraging the power of the Industrial Internet to help make significant savings, through the implementation of precision navigation services, flight data analytics, and fuel management. Through better efficiencies, AirAsia has set its sights on significant savings to the tune of up to $50 million over a five-year term.
4. Healthcare
As what they say, prevention is better than cure – and digital analytics has the potential to revolutionize healthcare in this aspect. A hospital management system that combines smart sensors, location-based tracking, wireless technology and cloud computing can help to optimize the flow of patients, employees, equipment and medical supplies.
By embedding sensors-enabled devices in medical equipment, healthcare professionals will be able to monitor patients more effectively. They will also be able to figure out which patients to prioritize for attention – for instance based on the data gathered from wearables monitoring their condition. Through this network of devices, healthcare professionals can draw insights to create a system of proactive management.
At Aventura Hospital in the U.S., the patient tracking solution delivers real-time data to reduce the time patients spend in waiting rooms, as well as the time that doctors and nurses spend searching for equipment. This has helped cut down waiting time at the emergency department by 68 percent, where a couple of extra minutes saved can mean a world of difference to a patient’s condition.
We will also see hospital buildings and operations becoming smarter. GE is pioneering a robot system to sort and sterilise surgical tools automatically, reducing mistakes and freeing up staff resources.
The industrial digitization of machines, appliances, and everyday physical items is driving innovation in new technologies, applications and business models. Even at this early stage, IIoT is already making a real impact.
India is already taking steps in the right direction in its transformation to become a digital economy. In the government’s vision for a Digital India where IoT is set to play a pivotal role, GE’s digital industrial solutions are poised to empower businesses and organisations with the advanced form of data analytics and technologies to achieve better outcomes.
In order reap great benefits in future, we will need policies to promote interoperability, security and privacy rights, as well as encourage government and business leaders to embrace data-driven decision making.
And as we move into an increasingly hyper connected world, everyday life is set to be further changed in ways not yet imaginable.
Source: BloombergQuint