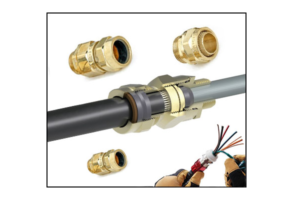
The members of the human race have made many remarkable inventions in the electrical field, of which one of the extremely critical and vital discovery have been in maintaining earth continuity, grounding or earthing system. Here, the success key to security lies in proven design and powerful interior component of cabling system that proves apt to get a secured earth continuity and grounding structure. Todays trending and one of the majorly used SWA cable has its application in underground systems, power networks, cable networks, cable ducting, outdoor and indoor application. For this, a rough & tough cable gland system is the name of the game to control and maintain the earth continuity at the time of armouring SWA cables. This article brings to light the importance of the BICC cable glands and its rich features that help in maintaining earth continuity while armouring SWA cables.
No doubt that electricity has provided numerous benefits to people, it also is a dangerous component that is being used in our daily lives. For a smooth electrical connectivity and safety of electrical system, the whole electrical system is grounded in addition to ensuring that the grounded circuit is electrically continuous. To protect your electrical assets or to control the power supply, proper earth continuity is required. Let’s get a short detail on earthing system.
As the electricity hunts for a smaller path back to earth, in case if any kind of problem occurs where the neutral wire is interrupted, the grounding system provides a direct path to the ground that can help save human life from an electric shock or avoids other disaster.
Nowadays, the steel wire armour SWA cables are highly used in the installation of the electrical systems. So the cable glands that are used in terminating the SWA cables needs strong and tough features. What role does a cable gland play in maintaining earth continuity while armouring SWA cables? How is the cable connector for the earthing system being structured? What is its importance? Is it specially called the SWA cable glands? These queries are outlined and made clear in the following content:
In usual cases, the cables are either connected to an earth tag, enclosures, gland plate or through an external earth path to be able to maintain the earth continuity when armouring SWA cables. There are different ways with which the cable gland is being structured with the SWA cables to get a safe grounding system.
One of the ways is the ‘direct to ground earthing’. Here, a cable is being earthed in at least one of the ends to achieve the direct path to ground. For this, many External Earthlink Cables are connected to the cable glands with an earth tag. Another way to structure a cable gland that can fetch smooth earth continuity while armouring SWA cables is the ‘daisy chain earthing’. Here, an earth tag through each cable gland is connected to external earth cable. Via earthing bar, each earth tag connects the earthing cable straightly to the ground. This method is majorly used when the non metallic instrument enclosure needs multiple cable entries.
The BICC cable gland manufacturer designs a tech savvy layout by adding required brass or aluminium slip in earth tags to a particular cable gland assembly. Both these techniques are used and best suited when it needs a low level of short circuit protection. Well! For higher or medium level short circuit protection, the cable glands high tech cast cable lugs or BICC cable lug is proven product for smooth installation.
Furthermore, to avoid corroded earthing connections and to get good earth connectivity while terminating an armoured cable properly, the researchers came up with an upgraded version of the base component of the cable gland that is ‘earthing nut’. These are used in earthing of non metallic and metallic enclosures. The core features of Earthing Nuts include easy installation, paint removal, drilling of earth bolts is not required, highly durable, ease in EMC shielding and above all it has smooth earthing on enclosures structured as per IP ratings.
On the other hand, at the time of armouring the SWA cables to the metal enclosures, there should be a firm mechanical and a sound electrical connection on the interface that is between the brass gland and the steel enclosure. Also an earth tag washer should be included in the cable gland assembly to ensure the steel enclosure and steel wire armour has a low resistance connection. While armouring the SWA cables to the non metal enclosures, the vital aspect involves a precise bend in SWA cable. It also includes an electric conductor of adequate size to maintain the continuity of armour across enclosures. In short, there exist varied methods and modified BICC cable glands to maintain the earthing mechanism while armouring the SWA cables.
For more information visit http://www.bicccomponents.uk.com/products/.