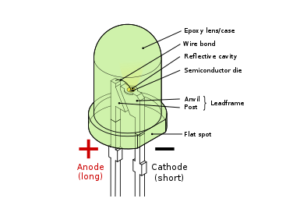
Light emitting diode (LED) is a special type of semiconductor P-N junction that under forwarding conditions can emit external spontaneous radiation in ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
LEDs have typical power to light energy conversion efficiencies approximately 10-50 times greater than of simple tungsten lamp. They have very fast response times approximately 0.1µs compared with ten or hundreds of millisecond for a tungsten lamp. So, they are widely employed as visual indicators and as moving-light displays.
Applications of LEDs:
The major applications of LEDs can be classified into three categories:
- Display LEDs: They are popular for numeric and alphabetic displays in watches, calculators, audio and video equipment etc. LEDs are also used for signal display such as ON/OFF switches or pilot lights for instrument panels.
- Fibre-Optic communication: LEDs can be used as a light source in optical fibre communication.
- The light source in a source-detector package: LEDs are used as a light source in smoke detectors, tachometers, proximity detectors etc.
Advantages of LEDs:
- Low working voltages (1 or 2V) and currents (5-20 mA).
- Less power consumption (10-150 mW).
- Very fast in action (response time of 10 nanoseconds).
- Small size and weight.
- Extremely long life.
- High reliability.
- Available in a variety of colours such as red, green, yellow, orange and infra-red.
- Can be given any desired shape.
Comparison of LED and Photodiode:
LED
- It is a light emitting device.
- It is always forward-biased.
- Electric energy is converted into light energy.
- GaAs or GaP or GaAsP are the material used for fabrication.
- Light is emitted due to the recombination of electrons and holes.
- Radiated power changes due to changes in temperature.
- Used as display devices, fibre optic communication and light source in a source-detector package.
Photodiode
- It is a light detecting device.
- It is always reverse-biased.
- Electric current is produced which is proportional to light.
- Fabrication is done using Silicon.
- Generation of electron-hole pairs results in flow of photocurrent.
- Photocurrent and dark current vary due to changes in temperature.
- They are used in fibre optics, optocouplers etc.